Both Fortinet and Palo Alto Networks are well regarded Zero Trust network access providers. In this article we’ll compare and contrast these two leading ZTNA vendors, with the goal of helping companies decide which option is best for them.
Zero trust security refers to a tightly controlled approach to providing access to IT infrastructure – no employee is provided access to any IT resources by default, and complete authentication is needed at every stage.
The working principle of the zero trust framework is based on the culmination of several technologies, including cloud security, authorized access, user validation, device authentication and endpoint security. While zero trust security as a concept has been around for many years, it is finally gaining traction as a technology product.
The growth of remote and hybrid workforces and the increased threat of unfiltered access to IT infrastructure has led enterprises to look at zero trust platforms with keen interest. The benefits of purchasing an enterprise zero trust platform include:
- Elimination of organizational risks.
- Superior access management over cloud environments.
- Elimination of data breach threats.
Read on to learn about the main features and differences between Fortinet and Palo Alto Networks.
Also see: Zero Trust Networking Solutions
How to choose a Zero Trust platform
Zero trust is an emerging approach to providing security to enterprise IT infrastructures, and as such its deployment varies considerably from vendor to vendor. The very idea of zero trust is defined somewhat differently by competing vendors.
To be sure, a solid zero trust platform ensures your IT resources are only accessible by authorized entities. But given that foundation, research the following:
- How is the multi-factor authentication deployed? Does it seem well-designed?
- What is the nature of the user interface? Zero Trust already provides challenges to users, and you want to minimize these for your staff as much as possible.
- A particularly important concern: what is the company’s ZT roadmap? Clearly, zero trust will evolve quickly in the years ahead. Will your potential vendor keep up?
We urge you to dive deeper into the features of Fortinet and Palo Alto, compare pricing packages and purchase a zero trust solution that most accurately represents your organizational necessities. And be sure to quiz those sales reps at length, don’t just read the product brochures.
Fortinet
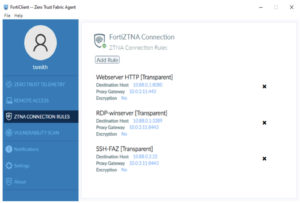
Fortinet Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a feature set within Zero Trust Access (ZTA) that enhances secure access to networks from anywhere. The zero trust platform extends the ideals of ZTA to verify devices and users prior to every application session.
Key Differentiators
- With flexible deployment capabilities, Fortinet ZTNA enables policies to be enforced for both on-premises and remote workers.
- Granular access control ensures access to a particular application only for that session.
- Verifies device identity, device posture, user identity and the user’s right to access an application prior to granting access to the application, with the help of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- A client-initiated model offers more control and visibility of an endpoint for the IT team while offering the user a simpler and quicker experience.
- Fortinet ZTNA is a free feature in FortiClient and FortiOS. Hence, you require no additional licenses to procure the zero trust platform.
- Automatically encrypted tunnels ensure traffic is hidden from probing eyes.
Palo Alto Networks
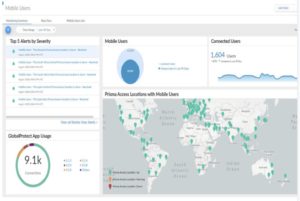
Developed by Palo Alto Networks, Palo Alto Prisma Access is a cloud-delivered ZTNA product that provides least-privileged secure remote access to services and applications. Prisma Access delivers threat detection, policy management, authentication and encrypted application access in a single solution.
Key Differentiators
- Provides identity-based access control to services and applications, with the help of MFA.
- Continuous post-connection trust and threat monitoring ensure services and applications are not exposed to threats.
- Simplified policy management makes it easy to control and manage the services and applications that on-premises, remote and mobile users are accessing.
- The zero trust platform offers consistent security while elevating productivity for an optimal user experience (UX) at scale.
- Other use cases include Cloud-based Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Next-Generation Cloud Access Security Broker (NG CASB), Firewall as a Service (FWaaS) and Autonomous Digital Experience Management (ADEM).
- Extend your enterprise security by acquiring the IoT Security and Enterprise DLP packages as add-ons.
Also see: 6 Enterprise Networking Security Trends
The post Fortinet vs. Palo Alto Networks: Zero Trust Platform Comparison appeared first on Enterprise Networking Planet.

