When a security vulnerability is discovered in software or network infrastructure code, it rarely makes sense to overhaul the whole product, especially due to the time, cost, and frequency of updates that would go into replacement code.
Software patches are typically implemented because they can address code vulnerabilities at a microscopic scale, targeting the actual point of problematic code and “patching” it with updated code until a new version of the product is available. Major tech vendors and open-source communities release patches for their software on a regular basis to secure their products and protect their enterprise customers.
The biggest problem that enterprises face with patching is keeping up with the latest patches and security vulnerabilities for their enterprise environment. Patch management software can assist administrative teams by helping them to monitor network anomalies, test patches before wider deployment, and deploy needed patches to all enterprise devices either automatically or on-demand.
Read on to learn about how patch management works and the differentiators offered by top patch management vendors in the market.
What is Patch Management?
Patch management focuses on monitoring and auditing enterprise network infrastructure for potential security vulnerabilities. Patches, or small code updates, can be applied to different parts of the network to make them run more efficiently or securely. Areas that can be patched include operating systems, applications, and servers.
Patch management is one piece of a greater vulnerability management strategy. A strong patch management solution helps vulnerability management to succeed in all of its phases: identification, reporting, prioritization, and remediation.
Learn more about security monitoring: Best Open Source Network Monitoring Tools
How Does Patch Management Software Work?
Patch management software itself typically uses constant security monitoring, industry security benchmarks, and granular dashboards to help security teams identify and patch code vulnerabilities. When working with patch management software, a patching team will typically follow this order of operations:
When a vendor releases a patch
Patch management typically starts at the tech vendor level. When they identify a code or performance problem in one of their products, their developer teams will work together to develop and test a strong patch.
After an extensive approval and documentation process, they’ll incorporate it into a new point or patch release for customers and announce it to their customer base. For especially crucial updates, they may automatically deploy the patch across user subscriptions after making their announcement.
Tech vendors often release these patches to patch management vendors directly. Patch management software typically includes a catalog of patches that have been shared with the patch manager, especially if the patch is related to one of the platform’s supported operating systems, like Linux or Windows. The patch management software can now alert users about the new patch and give enterprise teams different deployment options.
When an enterprise team develops a patch
In many cases, internal security or IT teams will identify a problematic section of code on one of their portfolio applications. Instead of waiting for a point release from the product vendor to improve the situation, they may take the following steps, in partnership with patch management software, to create their own patches:
- Apply continuous security monitoring: Patch management software uses security audits, scanning, and security monitoring on an ongoing basis to identify bugs and other systems issues.
- Developer teams code: When a problem is identified, developer teams brainstorm and write the code for a patch solution.
- Patch testing phase: The patch is tested in a sandbox or other non-active environment, and the patch simultaneously goes through an approval process.
- Documentation process: Once the patch has passed sandboxing and the approval process, documentation is written to explain and support the update. This documentation may also offer best practices about where, when, and how to deploy the patch for enterprise devices.
- Patch release to users: When an enterprise decides their patch is ready for wider user deployment, they’ll usually rely on the patch manager’s administrative dashboard to help them with deployment. They may automatically push the update to all user devices and affected applications. Or they may choose to use preformed groups and user profiles to release patches on an as-needed basis.
- Developers wait for feedback: Even for internal patch releases, developers should expect to receive feedback from their colleagues about how the patch works and if it has any functional issues. Sometimes, if developers aren’t careful, patches can cause new problems rather than solve old ones, so it’s important they listen to this feedback.
- The cycle repeats when a new patch need is identified.
Learn more about how patch management works today: Patch Management Trends for 2022
Features of Patch Management Software
The majority of patch management software solutions offer features that help with deploying externally developed patches, developing internal patches, and identifying code or performance anomalies that could be fixed with patching.
These are some of the most common features that patch management software includes for its enterprise customers:
- Sandbox testing environments
- Central server deployment, with remote deployment for a distributed workforce
- Systems inventory
- Regulatory compliance support
- Choice of automated or on-demand updates
- Patch, policy, and documentation templates
- Basic security monitoring and troubleshooting
- Third-party support and integrations
Also read: Five Tips for Managing Compliance on Enterprise Networks
Best Patch Management Software
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a cross-platform patch manager that supports Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems as well as over 350 third-party applications. This is a particularly strong solution for users that need to keep up with Windows 10 updates.
Features:
- Automated remote patch management through scanning, assessment, deployment, and reporting phases
- Customizable patch deployment policies
- Production environments for automated test group creation, test patching, and patch deployment
- Decline or postpone less important patches or patches that need to be revoked
- Real-time auditing and reporting
Pro: Many users have praised the speed, availability, and helpfulness of the vendor’s support team.
Con: Error messages are sometimes unclear or unavailable when a problem occurs on the platform.
Pricing: Free Edition, Professional, and Enterprise packages are all available to users. Pricing for Professional and Enterprise, both cloud and on-premises, can be found on ManageEngine’s pricing page.
Heimdal Security Patch and Asset Management
Heimdal Security Patch and Asset Management is a preferred patch manager for users who want support for policy creation, policy and documentation deployment, and general compliance. This tool offers CVE and CVSS audit trails and also integrates with Active Directory groups for easier user-level policy management.
Features:
- Advanced patch scheduling across time zones and machine types
- Vulnerability, patch, and group policy management across Windows and Linux
- Automated patching for over 100 third-party applications
- HTTPS encapsulation ensures the security of data-in-transit
- Infinity Management add-on for automated patching and flow updates with command-line scripting
Pro: Many users comment on the quick and effective rollout process for end-user patch availability.
Con: Some users have commented on the difficulty of initial configuration with this platform.
Pricing: Pricing information is not provided on the Heimdal website. Prospective customers should contact the Heimdal sales team for pricing information.
Syxsense Manage Patch Management
Syxsense Manage Patch Management is hosted in Microsoft Azure and provides patch management support for Windows, Mac, and Linux users. This is another strong solution for industry compliance needs, especially for HIPAA, SOX, and PCI compliance. Many users select this tool for the flexibility it offers in patching schedules and patching windows.
Features:
- Dashboards with Windows 10-specific patching data
- Device health with CVSS scoring
- Patch prioritization based on risk scanning results
- Automated deployment schedules with maintenance windows and recurring events
- Third-party patching natively available for Adobe, Java, and Chrome
Pro: Administrators like that they can create custom schedules and plans for patching that differ across teams and roles.
Con: Some users find that remote administrative controls are not as reliable as they could be.
Pricing: This patch management solution is one component of the larger Syxsense Manage product. Prospective customers should contact the Syxsense sales team directly for pricing information.
GFI LanGuard
GFI LanGuard offers integrations with over 4,000 security applications across antivirus, firewall, backup, encryption, access management, and data loss prevention categories. GFI LanGuard can run in either agentless or agent-based mode and supports Microsoft, Mac, and Linux operating systems. Many users like the flexibility of automated or on-demand system scanning and patch rollback.
Features:
- Third-party patch management and automation support for Apple QuickTime, Adobe Flash Player, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Apple Safari, Opera, and Java Runtime
- Threat level indicator graph for device vulnerability status
- Web-based reporting with HTTPS
- Vulnerability assessment database that is auto-updated to align with Microsoft security updates
- Virtualization and virtual machine compatibility with VMware, Microsoft Virtual Server, Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix, and Parallel
Pro: Security audits offer comprehensive historic data through an interactive dashboard.
Con: Some users have experienced system downtime or timeouts during particularly robust patch updates.
Pricing: GFI LanGuard is offered in three different pricing packages, based on the number of nodes needed: Small, Medium, and Large. Their prices range from $10 to $26 per node per year. Learn more about GFI LanGuard pricing.
Avast Business Patch Management
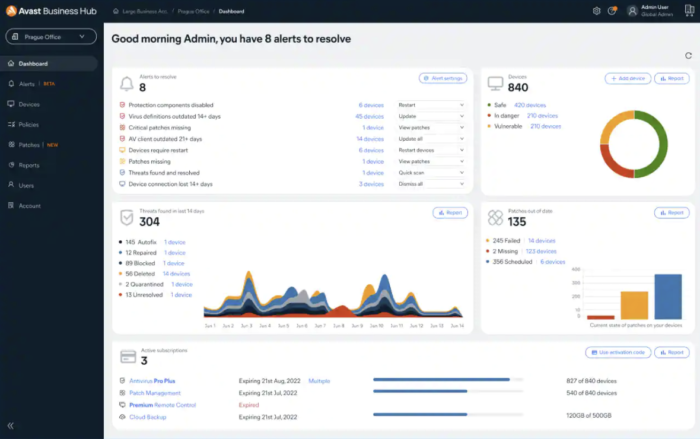
Avast Business Patch Management supports patching for Microsoft Windows and many popular third-party business applications. Some of the vendor applications for which Avast offers comprehensive patching support include Java, Adobe, Oracle, and iTunes.
Features:
- Remote patching and patch discovery
- Centralized dashboards and easy configuration for reports
- Automated patch scanning and deployment scheduling
- Patch rollback at individual device level
- Master agent management and patch distribution
Pro: Many users find the Avast Business Patch Management dashboard’s data visualizations to be highly intuitive.
Con: This product is limited to Windows users who also use Avast antivirus software.
Pricing: Pricing for Avast Business Patch Management ranges from $13.49 to $15.49 per device per year, depending on the number of devices covered.
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management
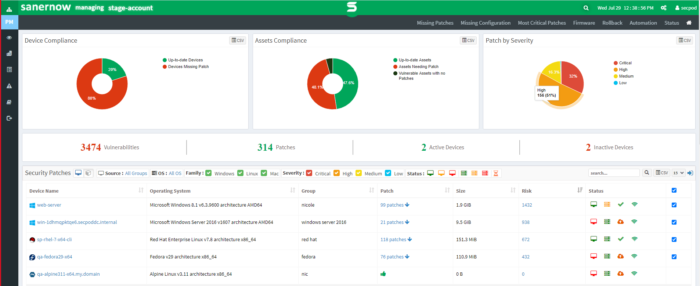
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management is a cloud-based patch management console that offers granular role-based access. It is compatible with over 300 third-party applications and all major operating systems. Many users choose this patch manager because it does not require a lot of overhead system resources to run and minimally disrupts business operations.
Features:
- End-to-end task automation for scanning, prioritization, download, testing, and scheduled deployment
- Customized real-time and continuous scans for verified patches
- Effortless rollback for an error-prone software patch
- Firmware patching for risk mitigation
- Auto-generated reports and native audit logging
Pro: Users like that this solution is lightweight and relies on less memory than several competitors, which makes it especially quick.
Con: Some customers have requested more customizability for dashboards and reports.
Pricing: Prospective customers should contact the SecPod sales team directly for pricing information.
Automox Patch Management
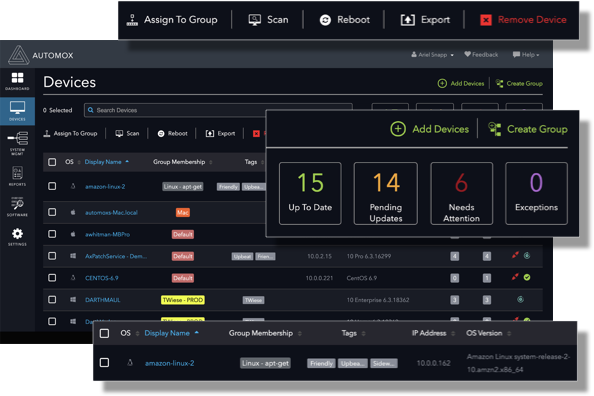
Automox Patch Management is a helpful patch manager for security teams that want detailed visibility and stronger administrative controls across enterprise assets. This software solution gives visibility into pending patches across user devices and applications. It also gives administrators the ability to remotely approve, reject, or investigate these pending patches.
Features:
- Single cloud console for hardware, software, patch, and configuration inventory management
- Support for deployment and rollback of third-party software
- Patch vulnerability and misconfigured system remediation
- Asset and inventory management with policy filtering and management
- Native third-party software catalog and custom scripts available for patching
Pro: Users compliment the detailed reports and policy management features available to administrators.
Con: Some customers have had trouble with certain Linux-specific patching features, such as onsite caching.
Pricing: Automox offers a Patch and a Patch & Manage plan. The Patch plan is $3 per device per month, billed annually. The Patch & Manage plane is $5 per device per month, billed annually.
Atera Patch Management
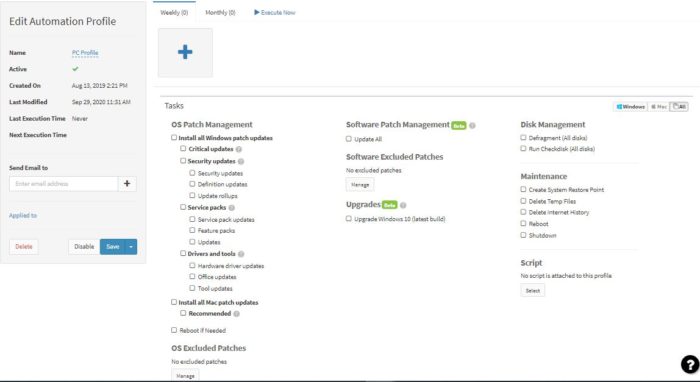
Atera Patch Management primarily offers patching for Mac and Windows, through Chocolatey for Windows and Homebrew for Mac devices. One of the product’s most highly praised features is its Shared Script Library, which offers script templates that have been vetted and created by both Atera and their managed service partners (MSPs).
Features:
- Three major reporting approaches available: Patch Search and Deploy, Patch Status Summary, and Patch and Automation Feedback
- Patching solutions natively available for applications like Chrome, Zoom, Skype, Dropbox, and Java
- IT automation profiles designated to each customer
- Automated software installations, updates, and reboots
- Shared Script Library with 100+ clonable scripts
Pro: Users appreciate the accurate and timely alerts this solution provides across IT infrastructure.
Con: Because Atera Patch Management cannot be bought without the other modules in the Atera platform, many consider this patch management solution to be too expensive.
Pricing: Atera Patch Management software can only be purchased as part of the entire Atera platform. Atera offers three main packages. Pro is $79 per user per month, Growth is $119 per user per month, and Power is $149 per user per month.
Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management
Ivanti Neurons for Patch Management mostly focuses on cloud-native patch management, but because of its previous focus in on-premises patch management, it’s a preferred solution for many enterprises that are still working through a cloud transition or in hybrid cloud environments. Ivanti gives these users a single dashboard pane to manage both cloud and on-premises patching needs.
Features:
- Vulnerability threat context and known exploit intelligence
- Crowdsourced social sentiment data and anonymized deployment data
- Cloud-native patch management with transitional support for on-premises patch management needs
- Autonomous Patch Configurations for distribution of tested patches
- Patch prioritization based on risk exposure, path reliability, and device compliance
Pro: Ivanti offers vulnerability risk rating (VRR), which is considered by some to be a better risk measurement solution than the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) offered on other platforms.
Con: Initial setup and permission settings for multiple administrators can be a difficult task.
Pricing: Pricing is available upon request from the Ivanti sales team.
Enterprise Benefits of Using Patch Management Software
Support for regulatory compliance
Patch management software is designed so that enterprises can keep up with security patches across all of the business applications they use. Some patches are simply designed for improved performance and efficiency, but many patches are designed for greater security.
Especially in highly regulated industries, like healthcare or financial services, companies can be severely penalized if they do not apply new security patches in a timely fashion to protect their users’ data. Patch management software helps these companies stay knowledgeable about new patches and gives them the visibility needed to apply that patch across required devices, applications, and users.
Increased network uptime
An unpatched vulnerability or code error could eventually lead to an application or wider systems crash, especially in the case of a successful security breach. Patch managers increase network uptime by addressing these vulnerabilities quickly and creating code that is more efficient and/or secure.
BYOD support
Patch management software is one of many solutions that assist with bring your own device (BYOD) administrative management. With security monitoring and device inventories, even mobile devices that only join the network infrequently will be kept in the loop when a new patch is available. This ensures that no matter how or where users access your network, their device and its software security is accounted for and up to date.
Automated and timely updates
Enterprises that don’t use patch management software have to closely monitor when any of their vendors release a new patch, which takes up considerable time. Patch management software simplifies some of this process by cataloging patch updates and alerting customers when it’s time to patch. They also usually offer automated deployment options, so administrators can patch all necessary enterprise endpoints with limited manual work.
Product innovation opportunities
Because patch managers can help developer teams to create and deploy patches for a variety of reasons, many developers use these tools to patch for improved performance and new efficiencies. Features of existing products can be upgraded simply through a strategic patch.
Read next: Top Vulnerability Management Tools & Software
The post Best Patch Management Software & Tools 2022 appeared first on Enterprise Networking Planet.

